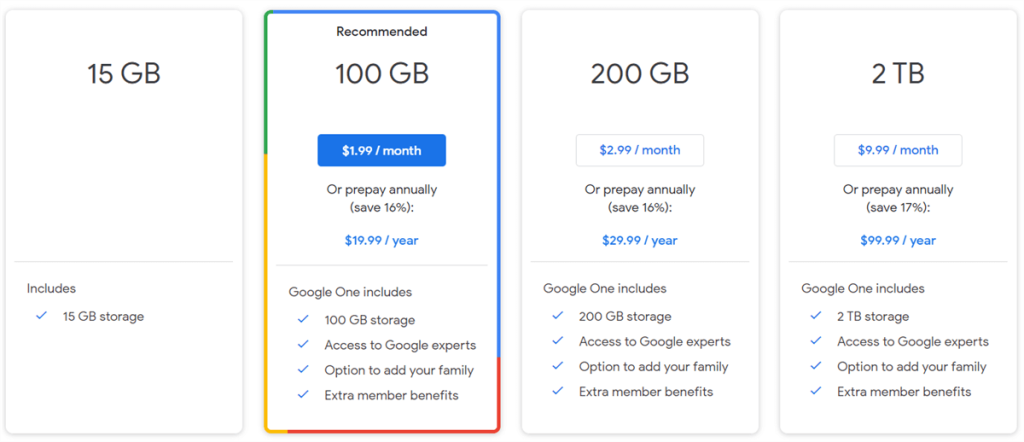
Google employs a freemium model, offering a basic level of service for free alongside paid options with increased features and capacity. The 15GB free tier functions as an entry point, allowing users to experience the benefits of Google Drive without financial commitment. This can entice them to explore paid plans if their storage needs grow.

Maintaining vast data centers for user storage incurs significant expenses in terms of hardware, software, and energy consumption. By limiting the free tier, Google controls its storage overhead, ensuring the service remains financially sustainable and scalable to accommodate its vast user base.
The 15GB limit might subtly encourage users to manage their storage effectively. This could involve:
- Deleting unused or outdated files: Regularly removing old emails, documents, and photos frees up space for newer and more relevant content.
- Utilizing storage-saving features: Google offers tools like “High Quality” in Google Photos, which reduces file size while maintaining acceptable quality, helping users stretch their storage further.
- Upgrading to paid plans: For users who consistently exceed the free tier, Google provides paid plans with increased storage capacities. This incentivizes users to invest in the service if it becomes essential to their workflow.

While 15GB might seem limited in isolation, it’s crucial to consider the broader cloud storage landscape. Many competitors offer similar or even lower free tiers, with paid subscriptions serving as the primary source of revenue. Google’s offering falls within the established industry standard.
Google argues that 15GB caters to the average user’s needs, particularly considering the dominance of text-based emails and the availability of storage-saving features. For most users, this capacity might be enough for storing essential documents, photos, and emails without exceeding the free limit.

In conclusion, Google’s 15GB free storage offering serves a multi-pronged purpose. It acts as a freemium model entry point, manages storage costs, encourages user engagement and management, aligns with industry standards, and caters to the basic needs of a significant user segment. While users with extensive storage needs might require paid plans, the free tier provides a valuable starting point for many users to experience the benefits of Google Drive.

This has many users wondering – why doesn’t Google simply increase this free storage allotment?
There are several factors at play in Google’s decision:
1. Cost and Resources of Google:
Maintaining vast data centers for user storage comes at a significant cost. Google, like any business, needs to balance the cost of providing free services with its need to generate revenue. Increasing the free tier would undoubtedly require significant additional investment in infrastructure and upkeep.

2. Encouraging Paid Subscriptions:
Google offers paid storage plans for users who require more space. By keeping the free tier limited, Google incentivizes users who need more storage to consider these paid options, generating revenue that helps offset the cost of maintaining the service.

3. Storage Management Encouragement:
The limited free tier might also be seen as a nudge for users to manage their storage effectively. This could involve deleting old emails, compressing photos, or utilizing alternative storage solutions for less frequently accessed files.

4. “Enough” for Most Users:
Google argues that 15GB is sufficient for the average user’s needs, especially considering the prevalence of text-based emails and the availability of storage-saving features like Google Photos’ “High Quality” option.
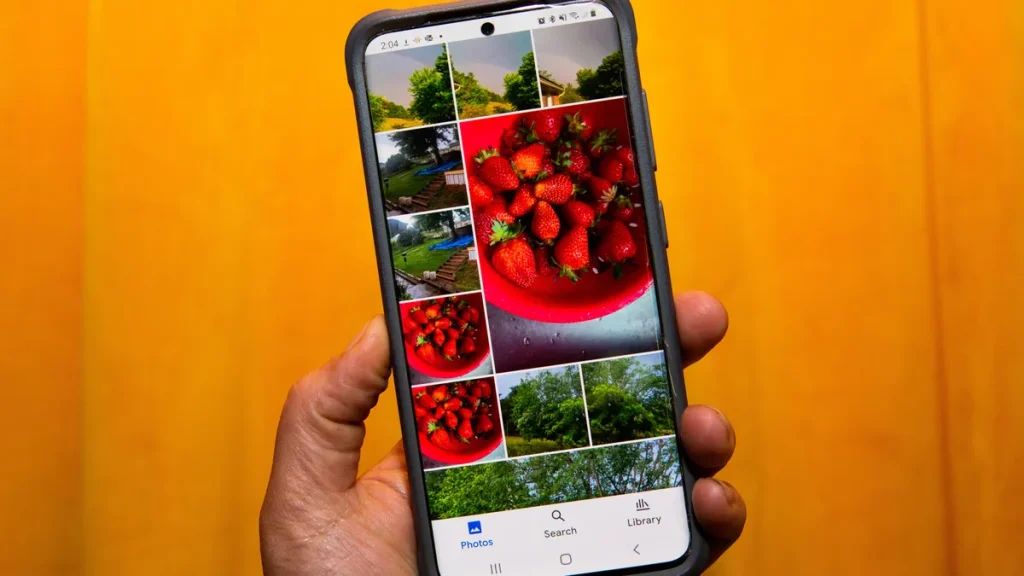
5. Competitive Landscape of Google:
While Google’s free tier might seem small compared to some competitors, it’s important to consider the broader context. Many cloud storage providers offer similar or even lower free tiers, with premium subscriptions as the primary revenue model.

Ultimately, the decision to increase the free storage tier lies with Google. While the company may face various pressures to do so, the factors mentioned above highlight the potential challenges and considerations involved. As technology evolves and user needs change, it’s possible Google’s stance on free storage might shift in the future. However, for now, users who require more space beyond the free 15GB will likely need to explore paid options or implement effective storage management strategies.





GIPHY App Key not set. Please check settings