Imagine a world powered by a clean, abundant energy source, replicating the very process that fuels the stars – nuclear fusion. For decades, this dream has remained elusive, existing primarily in the realm of science fiction. But today, with significant advancements and renewed international collaboration, the quest for nuclear fusion is heating up, offering a glimmer of hope for a sustainable energy future.
As a tech news veteran with over a decade of experience following the evolution of energy technologies, I’m here to delve into the fascinating world of nuclear fusion. We’ll explore the science behind it, the challenges scientists are tackling, and the potential impact it could have on our planet.
Unveiling the Secrets of the Sun: Understanding Nuclear Fusion

Nuclear fusion is the process that powers stars like our sun. It involves the merging of atomic nuclei, releasing enormous amounts of energy in the form of heat and light. Here’s a breakdown of the basic principles:
- The Building Blocks: At the heart of fusion lie atoms, the fundamental units of matter. Fusion focuses on fusing the nuclei of lighter elements, typically isotopes of hydrogen (deuterium and tritium).
- The Fusion Reaction: Under extreme heat and pressure, these hydrogen isotopes overcome their natural repulsion and fuse to form helium, releasing a significant amount of energy in the process. Imagine squeezing two grapes together so hard they turn into a watermelon, with a burst of energy released!
- The Challenge of Replication: Creating and sustaining the extreme conditions necessary for fusion – millions of degrees Celsius and immense pressure – is one of the biggest challenges scientists face.
Why Fusion? A Glimmer of Hope for a Sustainable Future
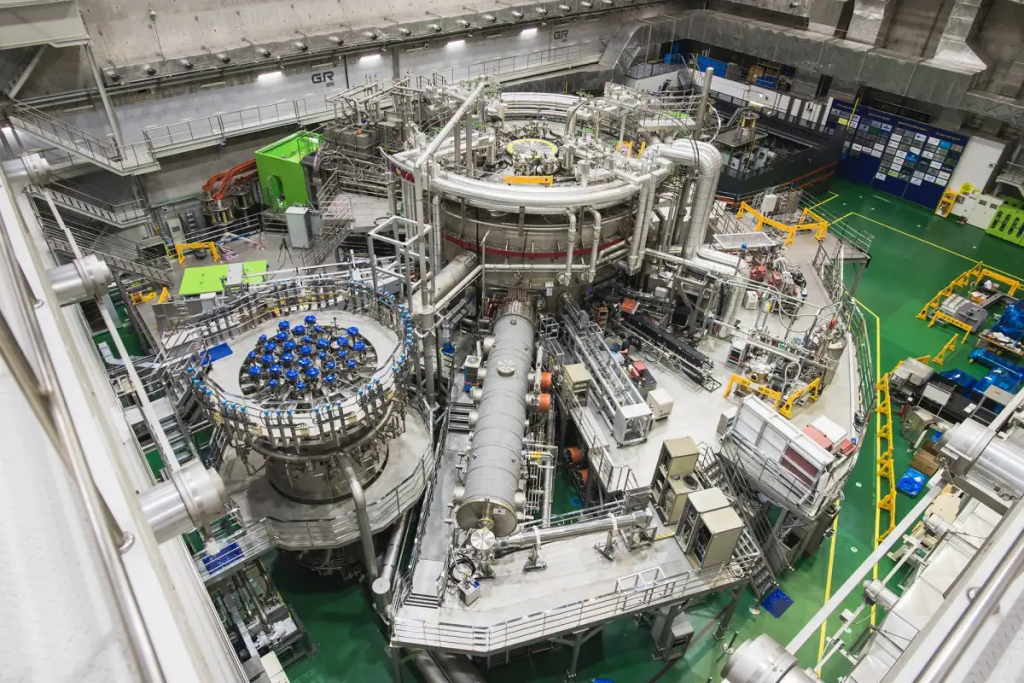
Nuclear fusion holds the potential to revolutionize the way we generate energy. Here’s why it’s so exciting:
- Clean and Sustainable: Unlike traditional nuclear fission, which uses heavy elements and generates radioactive waste, fusion is a clean process. It produces minimal radioactive byproducts and doesn’t contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
- Limitless Fuel Source: The fuel for fusion, hydrogen isotopes, is readily available in seawater. This ensures a practically limitless energy source, unlike fossil fuels which are finite resources.
- High Energy Output: A small amount of fusion fuel can produce a tremendous amount of energy, significantly exceeding the energy output of fossil fuels or even nuclear fission.
The Road to Fusion Power: Challenges and Advancements
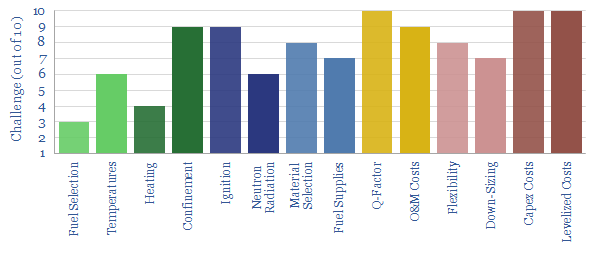
While the potential of nuclear fusion is undeniable, achieving a commercially viable fusion reactor remains a significant challenge. Here’s a look at some of the hurdles scientists are working to overcome:
- Creating and Sustaining Extreme Conditions: Maintaining the high temperatures and pressure required for fusion is incredibly difficult. Scientists are exploring various methods, including magnetic confinement and inertial confinement, to achieve this.
- Plasma Control: Fusion reactions take place in a hot, charged gas called plasma. Controlling the behavior of this plasma is crucial for sustaining the reaction and extracting energy efficiently.
- Material Science Challenges: The extreme conditions inside a fusion reactor pose a significant challenge for materials used to construct the reactor components. Scientists are developing new materials that can withstand these harsh environments.
Despite these challenges, significant advancements have been made in recent years. Here are some encouraging developments:
- International Collaboration: The ITER project (International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor) is a testament to global cooperation in achieving fusion. This massive project, involving 35 countries, aims to demonstrate the scientific and technological feasibility of fusion power.
- Record-Breaking Achievements: Research facilities around the world are achieving record-breaking fusion energy outputs, albeit for short durations. These milestones represent significant progress towards sustained fusion reactions.
- Technological Advancements: New technologies, like high-temperature superconductors and advanced computer modeling, are aiding scientists in designing more efficient and effective fusion reactors.
The Fusion Energy Landscape: Players and Players-to-Bei
The race for fusion power is a global endeavor, with various countries and institutions investing heavily in research and development. Here are some key players:
- ITER Project: This international collaboration is at the forefront of fusion research, aiming to build the world’s largest tokamak (a type of magnetic confinement fusion device) to demonstrate the feasibility of fusion power.
- National Fusion Research Laboratories: Individual countries like the US (DOE’s National Fusion Program), China (China National Nuclear Corporation), and Japan (Japan Atomic Energy Agency) have dedicated fusion research programs with significant facilities and resources.
- Private Companies: A growing number of private companies are entering the fusion energy space, bringing fresh perspectives and innovative approaches to the table. These companies aim to develop commercially viable fusion reactors on a faster timeline.
The Future of Fusion: A Brighter, More Sustainable Tomorrow
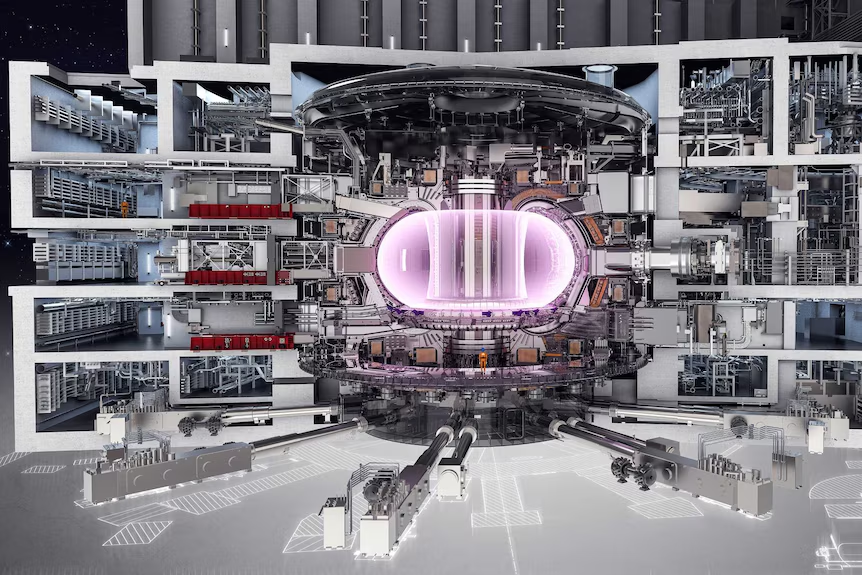
The future of fusion energy hinges on overcoming the remaining scientific and technological challenges. However, the potential rewards are immense, ushering in a new era of clean, abundant energy:
- A Greener Tomorrow: Widespread adoption of fusion power could significantly reduce our reliance on fossil fuels and combat climate change. By eliminating greenhouse gas emissions from energy generation, we can create a cleaner and more sustainable future for generations to come.
- Energy Security and Independence: Fusion offers the potential for energy independence, as the fuel source (hydrogen isotopes) is readily available from seawater. This can reduce reliance on imported fossil fuels and enhance energy security for nations.
- Technological Advancements Across Industries: The development of fusion technology can have ripple effects across various sectors. Advancements in materials science, plasma physics, and high-performance computing can benefit other branches of science and technology.
The Road Ahead: Collaboration and Investment are Key
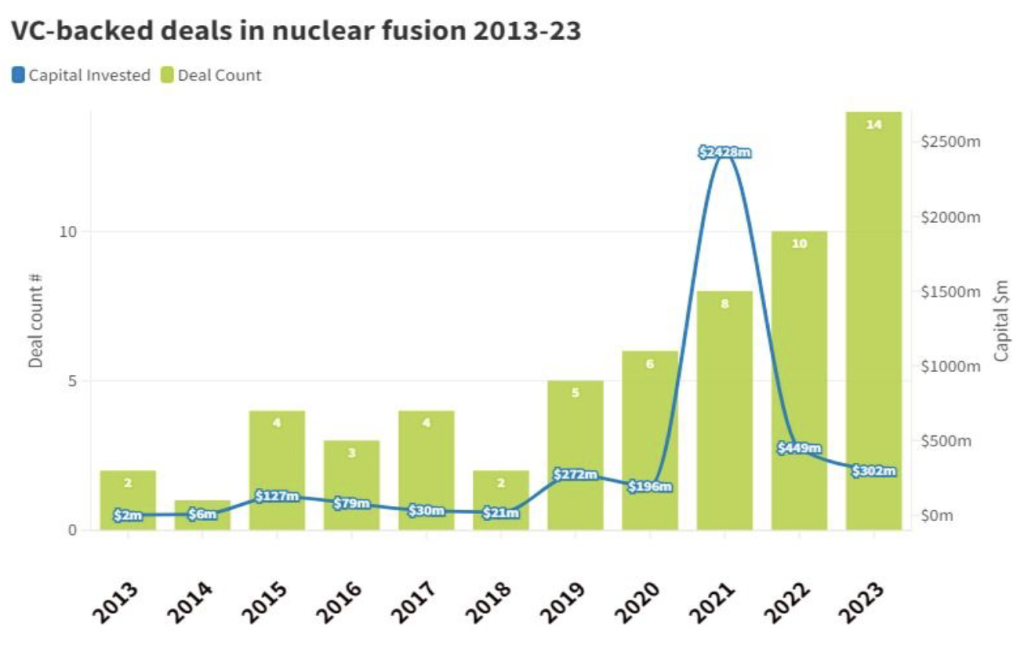
While fusion holds immense potential, achieving a commercially viable and scalable solution requires continued efforts. Here’s what needs to happen:
- Continued International Collaboration: Global cooperation, similar to the ITER project, is crucial for accelerating progress. Sharing knowledge, resources, and expertise can expedite the development of fusion technology.
- Increased Public and Private Investment: Significant investment is needed to sustain research efforts and build next-generation fusion reactors. Both government funding and private sector involvement are crucial for achieving commercial viability.
- Public Education and Outreach: Raising public awareness about the potential of fusion energy is essential. This fosters public support for continued research and development and encourages young minds to pursue careers in this exciting field.
The Final Word: A Dream Within Reach
Nuclear fusion is no longer a utopian science fiction concept. With dedicated research, international collaboration, and continued investment, the dream of clean, limitless energy from fusion power is becoming increasingly attainable. While challenges remain, the potential rewards are undeniable. As a tech news veteran, I’m truly excited to witness the future unfold as we work towards harnessing the power of the stars to illuminate a brighter, more sustainable future for our planet.





GIPHY App Key not set. Please check settings